Tungsten Carbide Flow Drill Bit



PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
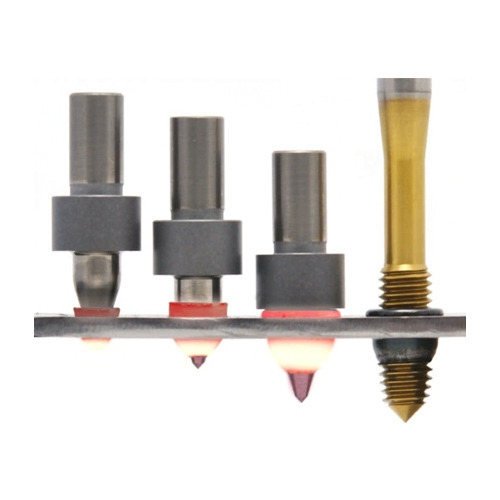
The principle of hot melt drilling
The hot-melt drill generates heat through high-speed rotation and axial pressure friction to plasticize and replace the material. At the same time, it punches and forms a bushing about 3 times the thickness of the raw material, and extrudes and taps through the tap to make it on the thin material. High-precision, high-strength threads.
RECOMMENDATION FOR USE IN WORKSHOPS
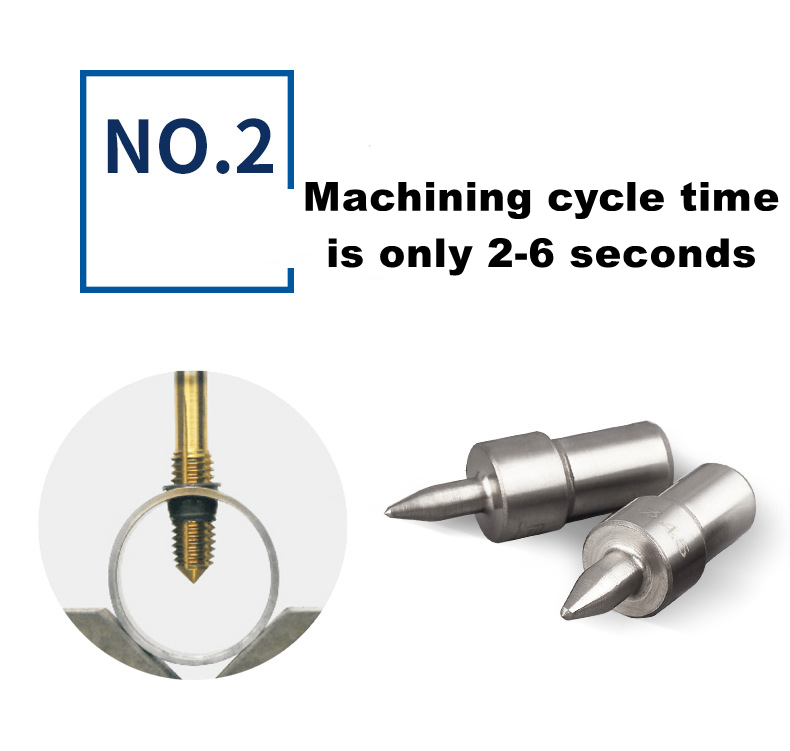
The first step: plasticizing the material through high-speed rotation and axial pressure. The thickness of the molded bushing is 3 times that of the raw material.
The second step: the thread is formed by cold extrusion to produce high-precision, high-torque and high-specification threads
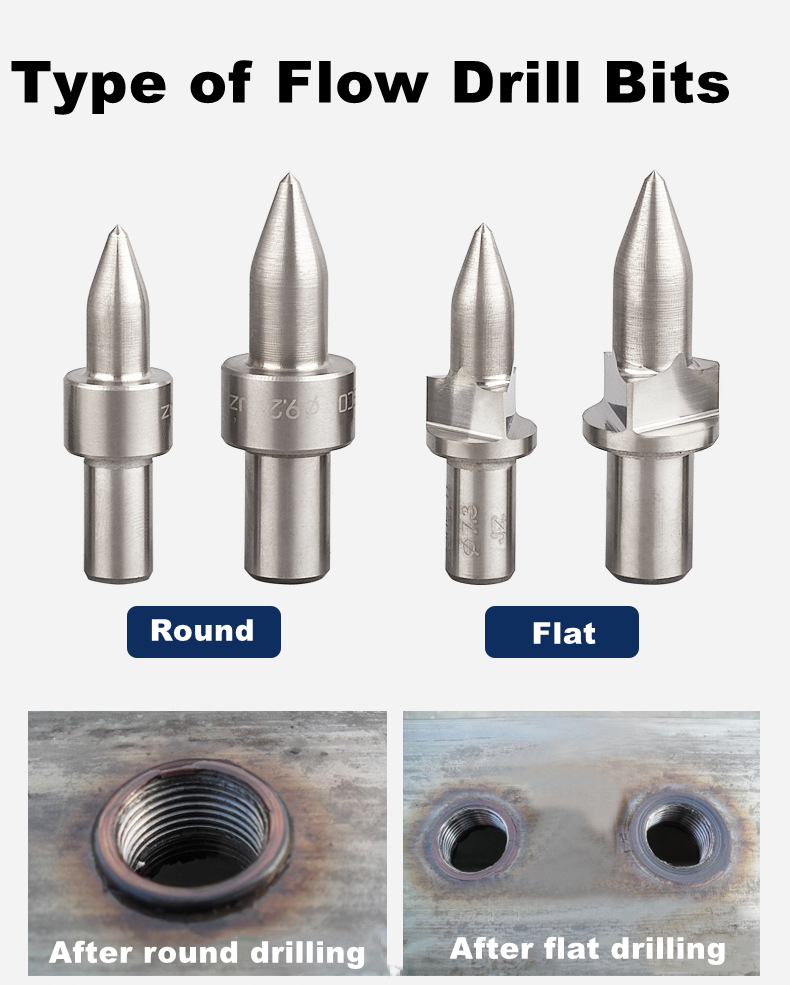
| Brand | MSK | Coating | No |
| Product Name | Thermal Friction Drill Bit Set | Type | Flat/Round Type |
| Material | Carbide Tungsten | Use | Drilling |
FEATURE






Precautions for the use of hot melt drills:
1. Workpiece material: hot-melt drill is suitable for processing various metal materials with a diameter of 1.8-32mm and a wall thickness of 0.8-4mm, such as iron, mild steel, stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, copper, copper, brass (Zn content less than 40%), aluminum alloy (Si content less than 0.5%), etc. The thicker and harder the material, the shorter the life of the hot melt drill.
2. Hot-melt paste: When the hot-melt drill is working, a high temperature of more than 600 degrees is instantly generated. The special hot-melt paste can prolong the service life of the hot-melt drill, improve the quality of the inner surface of the cylinder, and produce a clean and satisfactory edge shape. It is recommended to add a small amount of hot melt paste on the tool for every 2-5 holes drilled in ordinary carbon steel; for stainless steel workpieces, for each hole drilled, add hot melt paste by hand; the thicker and harder the material, the higher the frequency of addition.
3. The shank and chuck of the hot melt drill: If there is no special heat sink, use compressed air to cool down.
4. Drilling machine equipment: as long as various drilling machines, milling machines and machining centers with appropriate speed and power are suitable for hot-melt drilling; The thickness of the material and the difference in the material itself all affect the determination of the rotational speed.
5. Pre-fabricated holes: By pre-drilling a small starting hole, workpiece deformation can be avoided. Prefabricated holes can reduce the axial force and the height of the cylinder, and can also produce a flatter edge at the lowermost end of the cylinder to avoid bending deformation of thin-walled (less than 1.5mm) workpieces.
6. When tapping, use tapping oil: it is recommended to use extrusion taps, which are not formed by cutting but by extrusion, so they have high tensile strength and torsion value. It is also possible to use ordinary cutting taps, but it is easy to cut the cylinder, and the diameter of the hot-melt drill is different and needs to be made separately.
7. Maintenance of hot-melt drill: After the hot-melt drill is used for a period of time, the surface will be worn, and some hot-melt paste or workpiece impurities will be attached to the cutter body. Clamp the hot melt drill on the chuck of the lathe or milling machine, and grind it with abrasive paste. Do not pay attention to safety.










